Welcome to our guide on Stable Cascade, an innovative text-to-image model designed for efficient and powerful image generation. This article outlines how to utilize the Stable Cascade model, its architecture, and some troubleshooting tips to ensure smooth sailing on your journey. Let’s dive in!
What is Stable Cascade?
Stable Cascade is a generative text-to-image model that employs a unique architecture inspired by the Würstchen model. One of the key features of Stable Cascade is its significantly smaller latent space, which allows faster inference and reduces training costs. Think of it like downsizing an entire library into a cozy reading nook—everything is still there, but it’s more manageable and efficient!
Model Architecture and Details
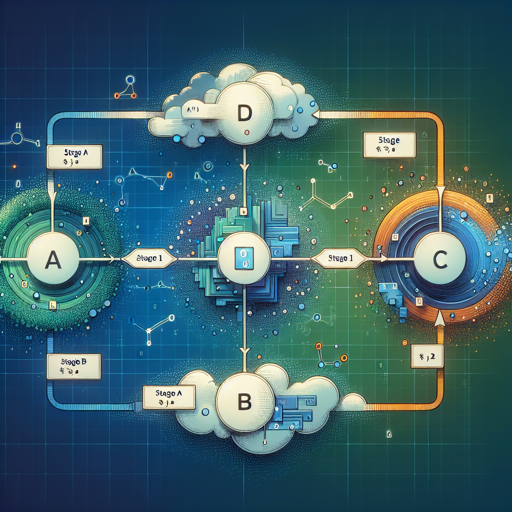
The architecture of Stable Cascade consists of three main stages, labeled Stage A, Stage B, and Stage C. These stages work together like a well-coordinated factory assembly line:
- Stage A & B: These stages compress images with a remarkable compression factor of 42, encoding high-resolution 1024×1024 images down to a mere 24×24 size while ensuring that the quality remains intact.
- Stage C: This stage generates the compressed latent images based on text prompts, completing the image generation process.
This architecture not only enhances training and inference efficiency but also allows for various extensions and modifications, making it well suited for applications where efficiency is paramount.
Getting Started: Code Examples
To get your hands dirty, you will want to implement the Stable Cascade model. Below is a basic example to get you started:
# Import necessary libraries
import torch
from diffusers import StableCascadeDecoderPipeline, StableCascadePriorPipeline
# Initialize your prompts
prompt = "an image of a shiba inu, donning a spacesuit and helmet"
negative_prompt = ""
# Load the model
prior = StableCascadePriorPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-cascade-prior", variant="bf16", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
decoder = StableCascadeDecoderPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-cascade", variant="bf16", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
# Execute the prior step
prior.enable_model_cpu_offload()
prior_output = prior(prompt=prompt, height=1024, width=1024, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, guidance_scale=4.0, num_images_per_prompt=1, num_inference_steps=20)
# Execute the decoder
decoder.enable_model_cpu_offload()
decoder_output = decoder(image_embeddings=prior_output.image_embeddings.to(torch.float16), prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, guidance_scale=0.0, output_type="pil", num_inference_steps=10).images[0]
decoder_output.save("cascade.png")
Utilizing the Lite Version
If you’re looking for a more lightweight method of rendering images, you can use the Lite versions of Stage B and C. Here’s how:
import torch
from diffusers import (StableCascadeDecoderPipeline, StableCascadePriorPipeline, StableCascadeUNet)
# Reuse your prompts
prompt = "an image of a shiba inu, donning a spacesuit and helmet"
negative_prompt = ""
# Initialize Lite models
prior_unet = StableCascadeUNet.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-cascade-prior", subfolder="prior_lite")
decoder_unet = StableCascadeUNet.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-cascade", subfolder="decoder_lite")
# Setup pipelines
prior = StableCascadePriorPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-cascade-prior", prior=prior_unet)
decoder = StableCascadeDecoderPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-cascade", decoder=decoder_unet)
# Execute the processes similarly as outlined above
prior.enable_model_cpu_offload()
prior_output = prior(prompt=prompt, height=1024, width=1024, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, guidance_scale=4.0, num_images_per_prompt=1, num_inference_steps=20)
decoder.enable_model_cpu_offload()
decoder_output = decoder(image_embeddings=prior_output.image_embeddings, prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, guidance_scale=0.0, output_type="pil", num_inference_steps=10).images[0]
decoder_output.save("cascade.png")
Troubleshooting Tips
As you navigate through the Stable Cascade model, you might encounter some hiccups. Here are some troubleshooting steps to consider:
- Ensure PyTorch Version: Make sure you have PyTorch 2.2.0 or higher installed, as certain features require this version.
- Model Offloading: If you face memory issues, enable CPU offloading for the model to optimize resource usage.
- Check Dependencies: Be sure all required libraries are installed and up-to-date to avoid compatibility issues.
- If problems persist, the community is ready to help you on your journey. For more insights, updates, or to collaborate on AI development projects, stay connected with fxis.ai.
Conclusion
The Stable Cascade model provides a revolutionary approach to efficient image generation from text prompts. By understanding the architecture and implementation, you can unlock its full potential for your projects. At fxis.ai, we believe that such advancements are crucial for the future of AI, as they enable more comprehensive and effective solutions. Our team is continually exploring new methodologies to push the envelope in artificial intelligence, ensuring that our clients benefit from the latest technological innovations.
Further Resources
For extensive research and code examples, don’t forget to check out the Stable Cascade GitHub Repository and the associated research paper.
Now, go ahead and unleash your creativity with Stable Cascade!